Urban Architecture: Implementing Efficient Water Tanks

Table of Contents
Water, being a lifeline in urban settlements, necessitates an efficient system of storage and distribution. The architectural design of water tanks plays a critical role to ensure the proper functionality of this system. A comprehensive understanding of water tanks from their design, materials, positioning to maintenance is crucial in implementing efficient urban architecture.
The Importance of Water Tanks
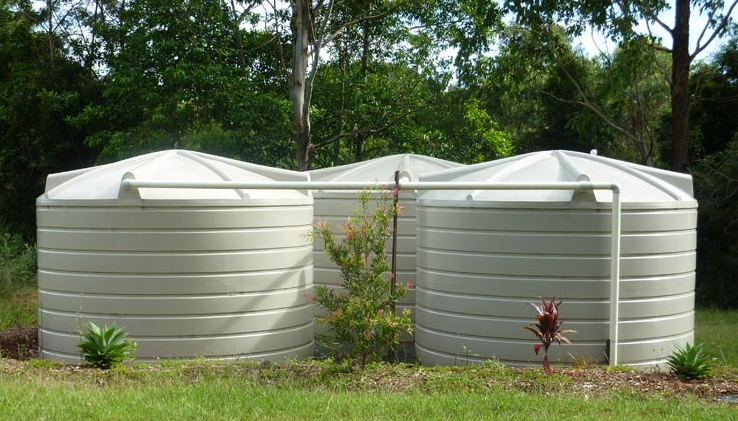

Water tanks play an integral role in urban areas, especially with the deepening global water crisis. They are the essential elements that help in managing clean water supply round the clock. Plus, they supply emergency backups during periods of drought or disruption in main water supplies.
Rainwater harvesting is also facilitated by these structures where collected rainwater can be stored for non-drinking purposes like flushing toilets and watering plants. Thus reduces the dependency on freshwater supplies, saving precious resources that are becoming more scarce.
With climate change and growing populations putting more pressure on limited water resources, efficient water storage and distribution via tanks is crucial for building resilience.
Essential Components of Water Tanks
The efficiency of a water tank majorly depends on its key components. It’s not just the tank alone but other critical components like booster pumps to ensure proper pressure, overflow pipes to maintain safety, and insulation systems for maintaining temperature.
In essence, each part of a water tank should be meticulously designed and installed to attain maximum efficiency and longevity in its service life. This also contributes to cost-saving in the long run.
Design Criteria for Urban Tanks
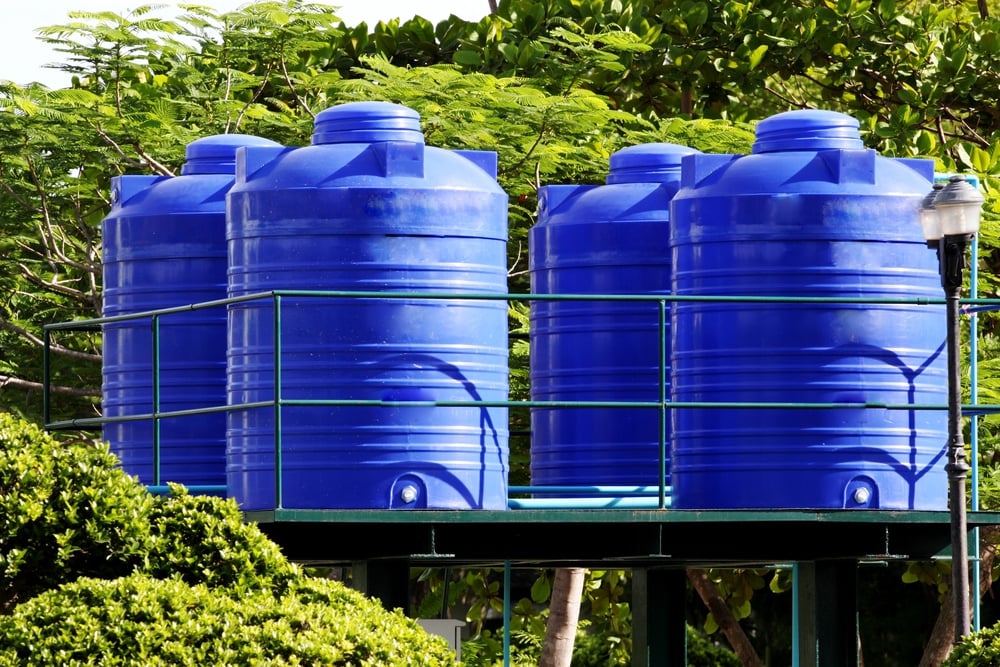

The design criteria for urban tanks should consider several guidelines about aesthetics, durability, capacity, and safety measures established by local governing bodies. Other considerations include the life expectancy of the tank and operation costs associated with it.
Ergonomic designs that take up minimal space yet provide maximum storage capacity could be a great solution for urban settings. Also, maintenance accessibility should be considered during the design stage.
Sophisticated technologies are transforming water storage systems in urban areas. For example, Sydney’s Water Tank Factory. uses progressive design and manufacturing techniques. Now, to find out more about their methods, click here.
Prefabrication and Construction
Prefabricated water tanks offer many time-saving benefits especially optimal for urban areas with busy schedules and strict deadlines. Factory-made parts are transported to the site and assembled there, a process that often requires less labor-intensive installation.
Moreover, prefabricated tanks boast high standards of quality control compared with traditionally-built tanks – errors are minimal due to machine precision on factory floors.
Maintenance of Urban Water Tanks
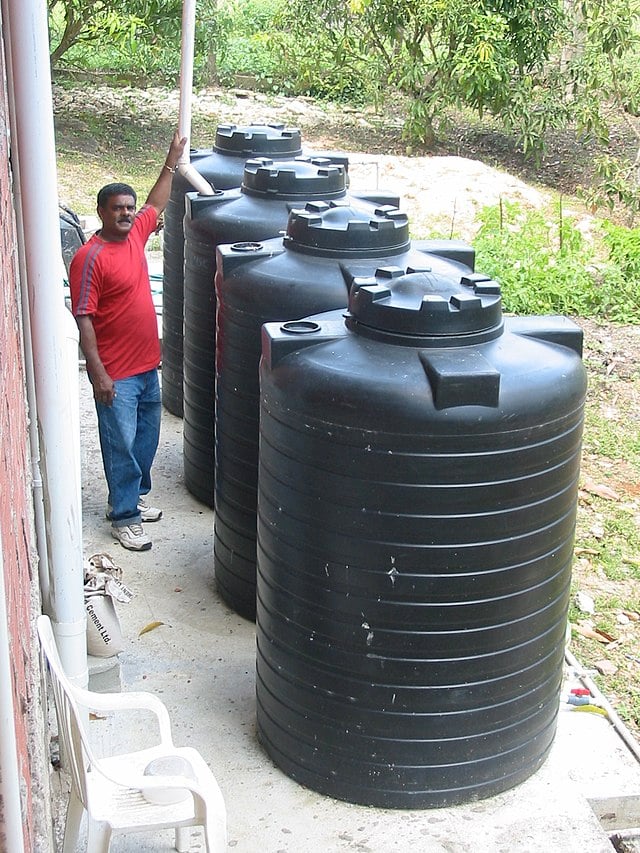

The maintenance of water tanks is equally important as its design and construction. Regular cleaning and inspection should be scheduled to ascertain the quality of water.
A poorly maintained tank can lead to water contamination causing health hazards. Therefore, ensuring that these structures are free from leaks and harmful buildup inside the tanks is vital for any urban infrastructure.
Urban Space Constraints
In ever-growing urban landscapes, space constraints are a common challenge. Effective use of available space without compromising the aesthetic value of an area becomes essential when installing water tanks.
Solutions can be found in innovative architectural design which includes underground tanks or slimline models that seamlessly blend into building profiles while also catering to spatial constraints.
Water Quality and Treatment
When it comes to urban water tanks, the safeguarding of water quality is of prime importance. Quality regulations ensure that only treated and safe to consume water is stored and distributed. Thus involving a multi-step treatment process.
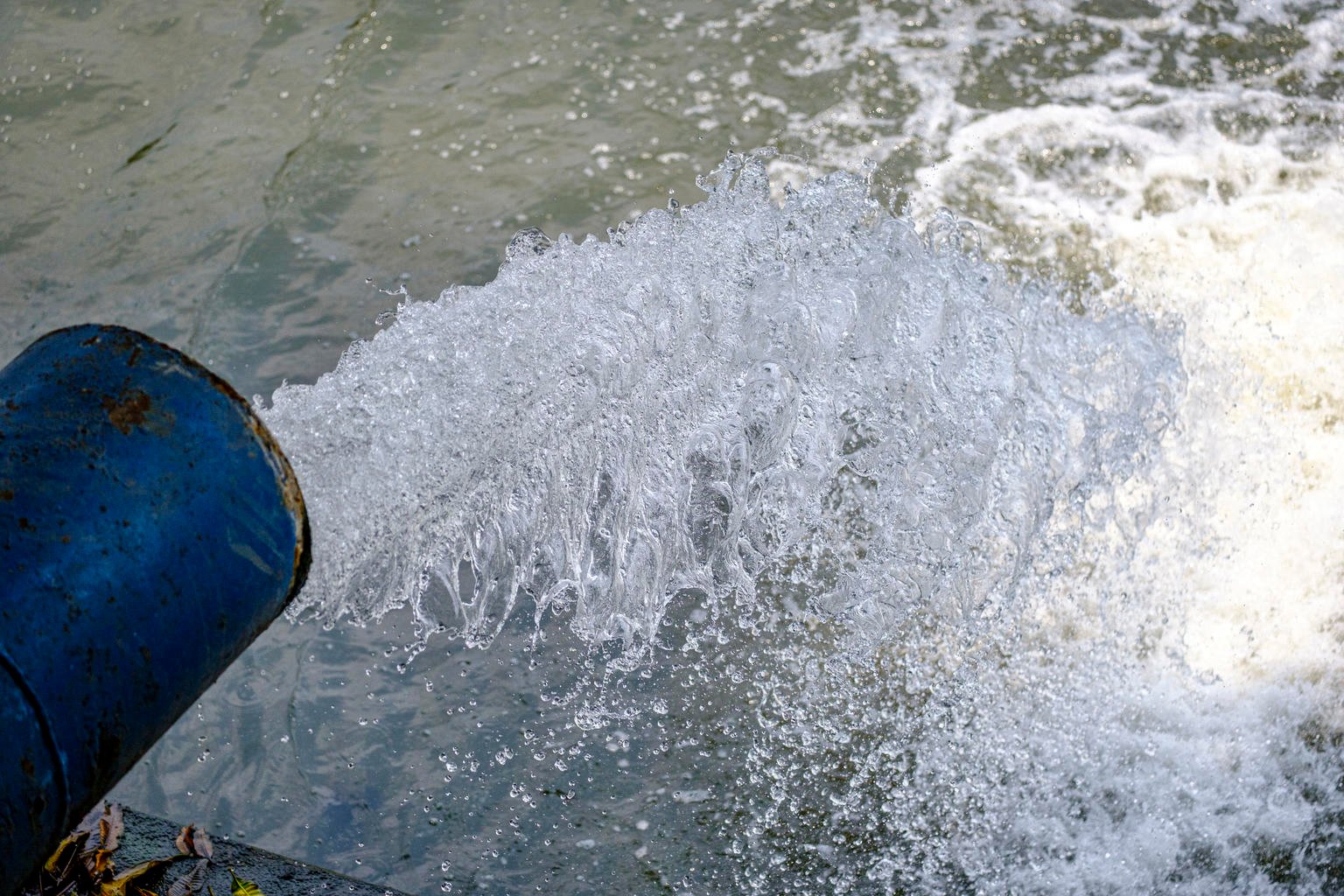

This process involves sedimentation, filtration, disinfection amongst others for removal of any harmful bacteria or viruses. In addition, during storage pH levels and temperature should be regularly monitored to avoid breeding of harmful pathogens.
Storage Capacity Planning
Before installing a tank central to urban architecture, precise planning of storage capacity needs to be assessed. It entails determining demand which can vary depending on the size and type of building that will utilize the tank.
Demand assessment must consider factors like number of residents, expected usage including contingencies for fire emergencies and droughts. Certainly, extra buffers are added in capacity projections for unforeseen circumstances.
Eco-Friendly Considerations
Eco-friendly considerations are becoming paramount when it comes to urban architecture decisions. Selecting materials that have minimum impact on the environment, encouraging rainwater harvesting, reducing reliance on natural freshwater sources, and ensuring energy efficient working of pumps are some examples.
Ideally water tanks should not add to thermal heat load and their design should allow deprivation of sunlight avoiding algae growth inside the tank. Moreover, efficiently designed tanks help in reducing energy usage thereby contributing towards carbon footprint reduction.
Urban Water Features
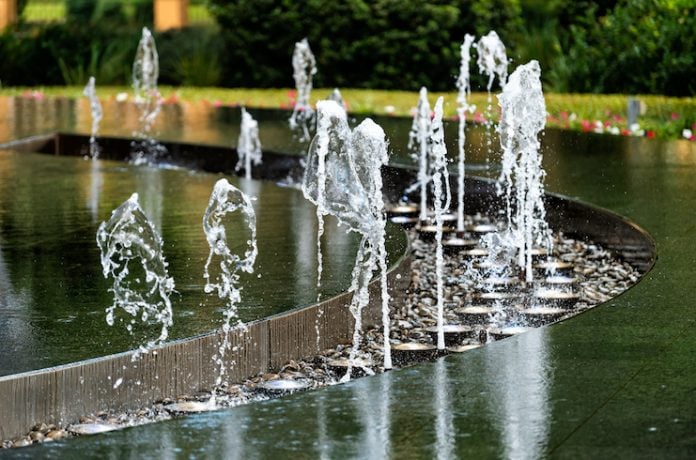

Urban water features like fountains and artificial streams add aesthetic value and curb appeal while facilitating rainwater harvesting for non-potable reuse like irrigation or washing cars. By incorporating water bodies into infrastructure, greywater availability is boosted leading to freshwater conservation.
Considerations when adding these features include catchment area, storage capacity, treatment systems, and landscape compatibility. Studies show such features provide psychological benefits as well by reducing stress and enhancing creativity.
Tank Positioning and Installation
The positioning of a water tank greatly affects its efficiency as well as influences the aesthetic value of a building. Ideally the installation position should provide easy access for maintenance, prevent direct sunlight exposure and not compromise architectural aesthetics.
Variance in local climate too dictates positioning – colder regions may require more insulated location while humid regions may need better ventilation. Underground or terrace are popular choices for urban setups.
Urban Green Spaces Irrigation
Urban farming needs efficient irrigation without wastage. Smart irrigation systems with soil moisture sensors can facilitate optimized watering schedules avoiding problems with overwatering. Drip irrigation delivers water directly to plant roots using tubing and valves, saving water versus sprinklers.
Soaker hoses leak minimal water on contact. Manual watering allows control per plant. Optimize methods based on garden size, plants, water pressure, etc. Integrate greywater harvesting and wastewater recycling to ease pressure on freshwater supplies. Precision micro-irrigation and reliance on recycled water vitally conserves drinking water amidst increasing urbanization.
Regulations and Standards

Building codes often regulate aspects like materials, design, and location of water tanks for safety purposes. Contractors should be well aware and comply with these fire and health standards to ensure consumer safety and avoid legal issues.
Typically, tanks should meet minimum capacity pertaining to life safety code i.e., fully sprinklered or partially sprinklered buildings. Additionally, quality standards must be adhered to avoid bacterial growth or any harmful contamination.
Funding and Cost Analysis
Before constructing a tank system, for example from a specialized Water Tank Factory, a critical cost analysis should be executed taking into account the potential maintenance costs, lifespan of tank material chosen, tank replacement costs along with initial construction outlay.
Furthermore, available funding options and grants for small-scale as well as large scale developments should be explored that can encourage loss reduction through energy efficient technologies thereby reducing long term costs. Partnering with an established Water Tank Factory can provide valuable insights into budgeting and financing options for installing new water storage systems in urban developments of varying scales.
To Summarize
Implementing efficient water tanks in urban landscapes greatly contributes towards sustainable urban development, ensuring uninterrupted water supply catering to varied demands of urban dwellers. The myriad factors from material selection, design efficiency to regular maintenance play a significant role making it a multifaceted challenge for architects globally.
Through active involvement of diverse technologies giving rise to innovative solutions, the goal of achieving highly efficient water management systems is feasible thereby ensuring resource optimization in growing cities.